A thoughtful goods distribution is crucial in the dynamic world of contemporary trade. For instance, placing books in high foot traffic areas is not only a choice for writers and publishers but a strategic imperative. This post will tell you everything you need to know about product distribution, from different distribution strategies to who is in the industry, so that you can refine your plan.
As well as improve your distribution strategy to achieve peak performance on the shelf. When expanding into new markets, the best brands know that staying on top of their entire sales process is critical to sealing the deal. But how can you stay on top of your sales process if you aren’t engaged in it each step of the way? Product distribution is one crucial step often overlooked by businesses.
Most brands choose the cheapest or easiest option rather than devising a legitimate distribution strategy. The influence of high-traffic areas is a significant opportunity for product distribution in high-foot-traffic regions because of the volume of prospective customers who pass through. Costco and airport shops are two highly sought-after locations that stand out for their excellent spots.
Especially for customer exposure and foot traffic. As business markets become more global, improving distribution is essential to ensure customers and all distribution channel members are happy. With that in mind, this revised guideline examines the solid justifications for the relevance of goods distribution in such regions and offers a tactical method for doing it successfully.
What An Ultimate High-Traffic Area Business Goods Distribution Plan Entails
High-traffic areas of goods distribution entail making a product available for purchase by dispersing it through the market. It involves transportation, packaging, and delivery. Distribution is fundamental to a company’s sales. A distributor purchases products strategically, stores them and then sells them through a distribution channel. They are between manufacturers and retailers.
Or consumers working on behalf of a particular company instead of representing themselves. Usually, distributors partake in collaborative relationships with clients and manufacturers. On the one hand, the right distributor enhances a company’s exposure in the product market and can give an edge in speed and efficiency. Notably, a distribution channel refers to the flow of business.
This occurs between a manufacturer and a consumer. It is the path that a transaction follows. On the other hand, distributors are the intermediaries that deliver and house products for producers to sell to retailers. These channels can be relatively simple or increasingly complex. There are direct and indirect channels. In a natural medium, the producer works directly with the consumer.
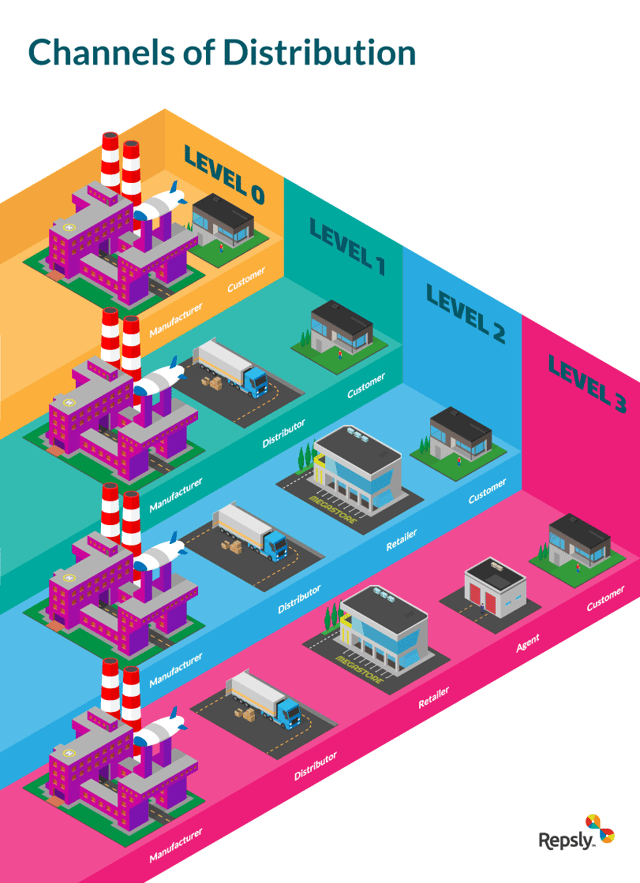
An indirect channel, on the other hand, incorporates intermediaries into the sales flow. Four levels break down the flow between manufacturers and consumers. You must know the different distribution levels to expand into new markets or switch up your distribution strategy. In other words, knowing your realistic product or goods distribution channels is crucial for your success.
Levels:
- Zero: A level zero distribution channel is the simplest. It involves a direct sale from manufacturers to consumers with no intermediary.
- One: A level one channel has one intermediary as the middleman between the producer and consumer. An example is a retailer between manufacturer and consumer.
- Two: When thinking about levels, associate the number with the number of intermediaries. In this case, a level two channel involves two intermediaries between the producer and consumer. An example would be a wholesaler selling to a retailer, then selling to the consumer.
- Three: Here’s where an agent or broker comes in. Agents work on behalf of companies and deal primarily with wholesalers. From here, the wholesalers sell to retailers, who then sell to consumers.
Sometimes, there tends to be a bit of confusion between what a distributor is and how distributors differ from wholesalers in the marketplaces. In general, a distributor works closely with a manufacturer to sell more goods and gain better visibility on these goods. For your information, on the one hand, distributors usually find product wholesalers to resell their business goods.
In contrast, a wholesaler works more closely with retailers to match their needs by buying products in bulk at a discount. Therefore distribution is an integral part of the distribution channel as it acts as the medium between the manufacturer and their customers. It’s one of the most significant elements in goods distribution management—the main product distribution activity.
It Includes:
- Products Packaging: Providing adequate packaging for a product to be transported safely.
- Inventory Management: Maintaining a reasonable inventory level is hugely important to distribution. Management of inventory is one of the primary responsibilities of distribution management.
- Order Processing: Once an order comes in from a customer, distribution management needs to plan for the delivery. This involves collecting the stock, loading it, and delivering it promptly. Approval must be sent and invoicing done for this step to be valid.
- Business Logistics: Mode of transport is critical to consider for all orders. If they require overseas shipping, there must be agreements for permits to be approved quickly. Loading and handling need to be decided so that all equipment that could be required is available onsite.
- Communication Tools: Clear communication is needed on and off-site at distribution centers. This ensures that the correct products are shipped and customers know when they will receive them. Distribution management must notify all interested parties immediately if a shipment is delayed.
It’s the activity of selling and delivering products and services from manufacturer to customer. Good distribution strategies often depend on the business product type being sold. Knowing what kind of distribution you need to achieve your growth goals is the trick. Three methods of distribution outline how manufacturers choose how they want their goods to be dispersed in the market.
They are as follows:
- Intensive Distribution: As many outlets as possible. Intensive distribution aims to penetrate as much of the market as possible.
- Selective Distribution: Select outlets in specific locations. This is often based on a particular good and its fit within a store. Doing this allows manufacturers to pick a price point that targets a specific market of consumers, therefore providing a more customized shopping experience. Selective distribution caps the number of locations in a particular area.
- Exclusive Distribution: Limited outlets. This can mean anything from exclusive luxury brands to special collections available only in particular locations or stores. This method helps maintain a brand’s image and product exclusivity. Some examples of companies that enact exclusive distribution would be high-end designers like Chanel or even an automotive company like Ferrari.
It’s important to realize that the chain of goods distribution can get confusing as more people are added. Distributors, wholesalers, retailers, and agents work as intermediaries in the sales process. As mentioned, distribution is selling and delivering products and services from manufacturer to customer. This can also be called product distribution as businesses become more global-centered.
Usually, most business products and goods distributor experts ensure products fly off the online marketplace and retail store shelves. For example, one distributor may work out an agreement with a famous beverage company that works with them regularly, whereas wholesalers are used need-by-need. They can sell directly to retailers and other sellers or consumers and businesses.
Improving distribution to ensure customers and all distribution channel members are happy becomes essential. Depending on the distribution channel length, many people can be involved in the distribution process. Below are the distribution channels to note:
By all means, distribution is an essential element of operations as, without a role that tracks and improves the relationship between manufacturers and customers, a company cannot ensure the best possible service. If bottlenecks happen in distribution, deliveries fall short, customers, retailers, and suppliers get angry, and trust is lost. Product distribution can be genuinely successful.
But a continuous feedback loop needs to be implemented to ensure everyone is happy with the process and that any improvements that can be made are made. Regarding a Dropshipping Business and customers buying items online, merchants and customers do not get to try the product before they buy, so they trust that the item will arrive, just like in the pictures and descriptions.
As a rule of thumb, the distribution channel must efficiently provide responses and comments across the whole track. Equally important, it is essential to know the critical differences between the individuals who play a role in the distribution process.
(a). Distributors
A distributor is a wholesaler who assumes extra responsibility. In addition to fulfilling retailer orders, they actively sell products on behalf of the producers. From managing orders and returns to acting as sales representatives, they go beyond being the middleman between retailers and producers. They perform market analysis and constantly search for new opportunities to achieve peak sales performance. A distributor focuses on a particular area and market, allowing them to cultivate strong relationships with manufacturers. Unlike wholesalers, they most likely have a stronger affiliation with specific companies they work with.
(b). Wholesalers
In this case, a wholesaler is a person or business that sells items to retail stores and then sells them to customers for a higher price. You could also call a wholesaler a distributor. They help fulfill retailers’ orders by reselling large quantities of goods for manufacturers. Wholesalers purchase in bulk, typically, which lowers the price, from either distributors or manufacturers. This allows wholesalers to profit because they can sell to retailers in smaller packages with higher prices. Unlike distributors, wholesalers only deal with the storage and delivery of goods. But, sometimes, you must go through a wholesaler to get to a distributor.
(c). Retailers
Notably, a retailer is a person or business you purchase goods from. Technically, retailers typically don’t manufacture their items. Instead, they buy goods from a manufacturer or a wholesaler and sell them to consumers in small quantities. Thus, retailers are the outlets where consumers can purchase products. This is your local grocery store or Walmart down the street. They can sell through storefront locations or online channels. Retailers buy products from distributors or wholesalers. Examples of retailers include supermarkets, department stores, specialty stores, convenience stores, and online stores.
(c). Brokers
Make way for your goods distribution agents. A broker is a person that facilitates transactions between traders, sellers, or buyers. Think of them as middlemen who ensure transactions run smoothly and that each party has the necessary details. Brokers exist in many industries, including insurance, real estate, finance, and trade. They handle the logistics of the sales. Agents handle contracts, marketing, and pulling together specialized shipments. A part of their job is customer relationship management. On behalf of manufacturers, they take ownership of products through the distribution process. They represent the producer in the sales process.
What A Distribution Management Process Entails With Dropshipping Examples
As Web Tech Experts, we strive to operate a product distribution channel that everyone profits from. Manufacturers, suppliers, and distributors can advertise their inventory in our partner marketplace, such as Oberlo, which is available to all merchants to browse and choose from. Merchants then select the products they want to sell in their online stores and add them accordingly. Learn more:
Eventually, once a customer purchases a product from the online store, the merchant is notified, and an order is placed with the distributor, who arranges for shipment from their facilities. This process is effortless with Oberlo as we listen to our merchants and distributors to make sure they are happy with the process. This also means we can improve our operations by fostering creativity.
As well as integrating new problem-solving techniques with our partners. Some businesses may also utilize E-Distribution strategies in their plan. To enumerate, E-Distribution is the electronic product distribution of things like digital downloads and software system applications. Such items include video games such as online slot games, computer software, eBooks, movies, NFTs, and music.
Slightly different from e-distribution and supply chain distribution, marketing distribution is how the marketing department makes products and services available to potential customers. Availability can be through the manufacturer, supplier, distributor, retailer, or wholesaler. From the perspective of the 4Ps of the marketing mix, marketing distribution can be slotted into the place category.
Examples of business goods distribution management channels:
- One: A manufacturer can employ a distributor to contact suppliers or retailers to purchase their product.
- Two: A supplier can make their stock available on a marketplace for merchants to find and sell.
- Three: A retailer could stock various products strategically placed across their store to entice customers to buy.
- Four: A wholesaler can build a website so customers can order products straight from them.
It’s important to realize that due to the ease of purchase and the immediate receipt of purchase, the e-distribution industry is fast-moving and highly profitable. Unlike physical distribution, e-distribution must be prompt for it to succeed. Customers who do not achieve a download link within minutes of purchase will contact suppliers to receive this. But there is always a worry!
Notwithstanding, the downside of this e-distribution is that it requires a constant internet connection to receive the goods. Also, file formats may lead to corrupt or usable downloads that cause customer dissatisfaction. Thus, a distributor must work closely with a manufacturer to sell more goods and gain better visibility on these goods. Distributors usually will find the best wholesalers.
The Top Best Strategic Approaches For High-Traffic Area Goods Distribution
When working with product distribution experts, brands oversee the process and prevent retail execution errors like stocks and distribution voids. This requires setting up clear lines of communication between managers, sales teams, and distributors to ensure you get that information as clearly and quickly as possible—brands on top of their game will form better customer relationships.
Particularly with their distributors and opening up expansion opportunities much more accessible than brands that communicate ad hoc. While email marketing and text messages may suffice for quick fixes, these won’t work long-term. Let’s say your sales rep informs you about an out-of-stock at location X. You might be able to remedy the situation by contacting your store distributor.
You can also consider ordering another shipment to that location. But if place X is continuously experiencing out stocks, the trend may fly under your radar if the only evidence you have is a few email threads buried deep in your inbox. Your random ordering pattern may make forecasting demand difficult or prevent distributors and retailers from receiving predicted shipments.
This is where data tracking and analytics become your best friend. Still, when you equip your team with the tools to constantly provide you with field insight, any recurring issues will become obvious much more quickly. Instead of receiving an email or text each time something was awry in the field, you received a data point that you could instantly compare to past data analytics.
Resource Reference: How Shipping Routes Can Affect An Online Ecommerce Business
You can then use the past data to identify any patterns immediately. Now, rather than your distributor having to constantly fulfill last-minute shipments each time location X experiences an out-of-stock, you can begin sending extra products with each scheduled shipment, making your and your distributor’s life easier. There are so many orders to fill and clients to keep up with.
Thus, having a data tracking system in place will make your and your distributor’s hard work worth it. Suppose there is a hiccup in the distribution network. In that case, you can glide past it quickly and maintain a consistent presence on store shelves, keeping distributors, retailers, and customers happy. Below are a few strategies to help in high-traffic areas’ goods distribution conversion.
1. Launching New Horizons
Of course, you can easily and quickly get your book into Costco; it’s a great chance. Costco draws a sizable crowd daily because of its enormous network of warehouses and membership structure. Your book will be exposed to a wide range of interested readers by being placed on the shelves of Costco, which will increase brand recognition, broaden your audience, and maybe increase sales.
2. The Costco Edge Strategy
Reputation, Authority, and Relevance are the rigorous selection steps that give Costco credibility. Getting your book authorized is an indication of quality and importance. This affiliation with a reputable company in the field raises the credibility of your book. Finding your book at Costco becomes a treasure hunt, turning reading into an adventure within a respected commercial hub.
3. The Journeys Start Points
In this case, you need a well-thought-out plan and strong marketing to get your book into airport stores. Airports attract a diverse audience, making them a perfect venue. Writing a compelling summary, creating eye-catching images, and showing recommendations all help to make your book attractive to readers looking for entertainment and information while traveling.
4. Relevance, Encounter, And Influence
Aeronautics Airports provide a unique platform for publications that stimulate readers’ minds throughout the hours spent traveling. Before leaving, finding a fascinating book makes a lasting memory. Airport shops choose their selections similarly to Costco, portraying your book as a high-end option and using the store’s good name to highlight the substance of your book.
5. The Link Between Placements
Your literary work is tightly entwined with the three core SEO principles: eminence, pertinence, and encounter. These pillars, which resemble the structure of deep thinking, are present in both the Costco emporium and the busy airport shopping areas. They demonstrate the interplay of these ideas via rigorous curation and carefully crafted tales, enhancing the prominence of your work.
Deciphering The Success Odyssey Steps For Business Product Distributors
It is not unreasonable to wonder why all products are not sold directly from the producer to the final consumer. The simple answer is that distributors lower the costs of market transactions in a specialized economy. First, distributors tweak the market transaction costs by taking advantage of economies of scale and scope. For example, retail stores typically offer many product varieties.
Firstly, it would be very costly for consumers to purchase every item directly from producers. Secondly, distributors reduce the information costs of market transactions. Wholesale merchants, traditionally, and retail merchants, more recently, lower the costs of trade by lowering the costs of discovering supply and demand conditions. Third, distributors also reduce the cost of work.
In particular, they do so by solving the asymmetric information problem. This problem typically arises when consumers cannot easily discern the quality of a product sold in the marketplace. Historically, wholesale merchants solved this problem by organizing exchanges that inspected quality and standardized grades. The traditional local retail merchants often solved this problem.
Eventually, this did so by developing a reputation for honesty. Over time, as market transactions became increasingly anonymous, multiunit chain retail stores and manufacturing firms used advertising and branding to solve the asymmetric information problem. However, the path to gaining a passage within these bastions of distinction and trade requires a plan of cunning intent.
Consider the following:
- Adding Tapestry Excellence: Your literary masterpiece is given a unique air through meticulous editing, captivating content, and appealing graphics.
- Weaving Enchanting Proposition: Concoct a proposition that highlights the distinctive elements of your literary work and resonates well with the sophisticated tastes of each locus’s target audience.
- Fostering Solid Interconnections: Take part in a symphony of industry gatherings, exposés, and galas to cultivate relationships with possible work distributors.
Ultimately, authors and publishers get a vital tactical value from the distribution method inside heavily populated citadels like Costco’s enclaves and airport outlets. The possible returns include increased brand awareness, a colossal literary following, and an increase in sales ascent using the broad expanse of exposure, the tapestry of credibility, and the relevance these enclaves provide.
Forward-thinking into the future, the execution of a product distribution strategy that prioritizes quality, uniqueness, and the art of network weaving will pave the route to a successful placement among these teeming centers of commerce and eminence.
In Conclusion;
Goods distribution is the activity of both selling and delivering products and services from manufacturer to customer. This can also be called product distribution. As businesses become more global, improving distribution ensures customers and all distribution channel members are happy. Depending on the distribution channel length, many people can be involved in it.
As mentioned, products and goods distribution are essential elements of any successful company operations as, without a role that tracks and improves the relationship between manufacturers and customers, a company cannot ensure the best possible service. If bottlenecks happen in distribution, deliveries fall short, customers, retailers, and suppliers get angry, and trust is lost.
For product distribution to succeed, a continuous business customer feedback loop must be implemented to ensure everyone is happy with the process and that any improvements can be made. Regarding any given dropshipping business and customers buying items online, merchants and customers do not get to try the product before they buy, so they trust that the item will arrive.
Eventually, this works effectively, just like in the pictures and descriptions. As the twentieth century progressed, wholesale merchants were squeezed from the other direction. Many large multiunit manufacturing firms began to market their products directly to consumers and retailers. Thus, the distribution channel must efficiently provide responses and comments throughout the track.
Some Answers To The Topmost Frequently Asked Questions
1. What’s the space purpose of wordsmiths and publishers in busy, high-pedestrian areas?
Wordsmiths are whose writing is eloquent due to the variety of vocabulary they can draw on when writing and speaking. They’re given the gift of exposure to a wide range of audiences by establishing a presence in high-pedestrian areas. Places such as Costco and airport shops, draw sizable crowds daily, elevating the visibility of literary works and possibly resulting in higher leads.
2. Why does breaking into Costco’s grounds carry such importance?
Because of Costco’s significant nexus and connection system, placing a literary work inside its walls exposes it to a broad public. The Costco screening process further boosts the book’s legitimacy, which adds to its stature. Customers’ discovery of a book within Costco transforms it into a special treasure hunt, adding to the allure of literary immersion.
3. How may wordsmiths add attraction to their creations to be desirable inside airway sanctuaries?
Being labeled as a wordsmith is a compliment. The key to creating a book that radiates appeal for residing inside airway bazaars is to craft a fascinating summary, conjure aesthetically striking pictures, and showcase essential endorsements. These elements are intended for wanderers looking for captivating stories to tell about their odysseys.
4. What benefits do writers get from the arrangement within airway havens?
Airline emporiums provide writers a unique payout by focusing on a confined group of travelers. Since travelers often seek intellectually intriguing reading material to pass the time, airline bookstores are a veritable stage for entertainment and education books. Still, airlines that can control costs can attract customers with lower fares and improve overall profitability.
5. How do the fundamental principles of SEO meet with busy, high-pedestrian areas?
Areas with high foot traffic are compatible with the three pillars of SEO: prominence, relevance, and engagement. The Costco domain and airline emporiums carefully filter their selections to ensure quality and suitability. Nestling a book inside these districts takes advantage of their notoriety, resulting in increased exposure and attention.
6. What are the key tactics for securing tenure in densely populated areas?
Make sure that your work is exceptional in both content and design. Create a Remarkable Proposal: Create a unique offering that appeals to the target market for each domain. Develop Networks and Forge Alliances: Attend industry mixers and expos to meet possible distributors and providers. Notwithstanding the type of tenure, all persons should possess a degree of security of tenure which guarantees legal protection against forced eviction, harassment, and other threats.
7. How might authors benefit from the spread of their books inside these neighborhoods?
The spread of books in areas with significant foot traffic may result in improved brand awareness, a larger readership, and increased sales. The importance and respect offered by these precincts aid in a literary work’s overall success.
8. Is it possible for independent authors to share the benefits of dispersion inside these dominions?
An indie author is a writer of fiction, nonfiction, or poetry books who self-publishes their work and retains and controls their publishing rights. Undoubtedly, precincts with high foot traffic provide visibility that may be profitable for both traditionally published writers and self-published authors. Flawless content, intelligent pitching, and network development are essential.
9. Are there any difficulties or problems with dispersing books in densely populated areas?
Though the potential rewards are significant, writers should consider factors like competition, allocation costs, and the need for vigorous promotional efforts. To overcome these obstacles, careful planning and execution are required.
10. How does the strategic strategy stated in this composition conclude in success?
Answer 10: The strategic plan emphasizes the importance of quality, uniqueness, and networking. By following these guidelines, writers may create works that exude originality, craft compelling arguments that resonate, and cultivate partnerships that ease distribution within high-pedestrian zones, eventually leading to increased notoriety and transactions.






Hi josephmuciraexclusives.com webmaster, Your posts are always well-structured and logical.
Hi josephmuciraexclusives.com admin, You always provide great examples and real-world applications, thank you for your valuable contributions.