In reality, Cyber Security Threats professionals (like jmexclusives) are continually defending computer systems against different types of cyber threats. Bearing in mind, various cyber-related attacks hit businesses and private systems every day. And, in recent times, a variety of such attacks has increased quickly. Hence, quick solutions are equally needed.
According to former Cisco CEO John Chambers, “There are two types of companies to consider more into this. Including those that have been hacked, and those who don’t yet know they have been hacked.” The motives for cyber attacks are many. One is money. Cyber attackers may take a system offline and demand payment to restore its functionality.
Ransomware, an attack that requires payment to restore services, is now more sophisticated than ever. Corporations are vulnerable to cyber attacks, but individuals are targets too, often because they store personal information on their mobile phones and use insecure public networks.
Related Topic: Website Security | 6 Tips To Secure Your Website Business
Tracking evolving and increasing cyber-attacks is the key to better managing and safeguarding cyber security. Today, many Cyber Security Professionals are tirelessly working to increase their knowledge of threats and cyber security information.
Bearing in mind, earning an online cyber security master’s degree can also be quite indispensable. As an example, Graduates of the University of Online Master of Science in Cyber Security Program can expect to gain a deep and nuanced understanding of cyber attack methods. That said, let’s now take a look at what Cyber Security Threats are.
What Are Cyber Security Threats?
Cyber Security Threats are malicious acts that seek to damage data, steal data, or disrupt digital life in general. Cyber-attacks include threats like Computer Viruses, Malware, Password Attacks, Data Breaches, Phishing, SQL Injection, Man in the Middle (MITM), Denial of Service (DoS), etc.
Opting to take advantage of the Cloud Hosting Service enables companies to access data from almost any location and saves both time and money. For example, many hosting providers offer their customers the possibility of saving or hosting both personal and commercial data in the cloud. As well as added security features.
In other words, a Cybersecurity Threat is a malicious and deliberate attack by an individual or organization to gain unauthorized access to another individual’s or organization’s network. More so, in the essence of damaging, disrupting, or even stealing IT assets. Such as computer networks, intellectual property, or any other form of sensitive data.
Notably, there are numerous Cyber Security Practices that continue to evolve as the internet and digitally dependent operations develop and change. According to Secureworks, people who Study Cyber Security are turning more of their attention to the two areas in the following sections. Namely, ‘The Internet of Things and Data Explosion.’
The Internet of Things
The Internet of Things (IoT), is a system of interrelated computing devices, mechanical and digital machines. As well as, objects, animals, or people that are provided with Unique Identifiers (UIDs), and the ability to transfer data over a network.
They do so without requiring human-to-human or human-to-computer interaction. In other words, when it comes to the Internet of Things, a thing can be just anything. For instance, a person with a Heart Monitor Implant or a farm animal with a Biochip Transponder.
Learn More: Internet of Things (IoT) | What Is It With Key Example Uses?
Because of IoT, individual devices that connect to the Internet or other Network utilities offer an access point for hackers. According to Cytelligence reports, back in 2019, hackers increasingly targeted smart homes and other Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
Such as smart TVs, voice assistants, connected baby monitors, and cellphones. Whereby, hackers who successfully compromise a connected home can gain access to users’ Wi-Fi credentials. They may also gain access to their critical data too. Such as medical records, bank statements, and website login information.
The Explosion of Data
The world is currently used to sparing everything without exception in the electronic space. Processing power, RAM speeds, and hard-disk sizes have expanded to a level that has changed our viewpoint towards data and its storage. Would you be able to envision having 256 or 512 MB RAM in your PC now?
By definition, “Data Explosion” is the rapid or exponential increase in the amount of data that is generated and stored in the computing systems. And, that reaches a level where data management becomes difficult to carry on with. So, how does it really work in terms of computing?
Related To Cyber Security Threats: How Students Can Protect Their Data
On the off chance that we comprehend the idea of byte, we can envision how data growth has expanded over time. And even how storage systems handle it. We know that 1 byte is equivalent to 8 bits — these 8 bits can represent character or expression.
An archive with a huge number of bytes will contain a huge number of characters, expressions, spaces, etc. Similarly, a Megabyte (MB) is a million bytes of information, a Gigabyte (GB) is a billion bytes of information, and a Terabyte (TB) is trillion bytes of information.
For this reason, we use these terms while managing data and storage, in our everyday activities. But, of course, it doesn’t end here. Next comes the Petabyte (PB), which is quadrillion bytes or million gigabytes. And, there are even more that come after that.
They include:
As for Yottabyte, it’s basically trillion terabytes of information. Technically, there are considerably even higher numbers to know about, but we’ll stop here for now. With that in mind, data storage on devices such as laptops and cellphones makes it easier for cyber attackers to find an entry point into a network through a personal device.
For example, in the May 2019 book Exploding Data: Reclaiming Our Cyber Security in the Digital Age, former U.S. Secretary of Homeland Security Michael Chertoff warns of a pervasive exposure of individuals’ personal information. After all, which has become increasingly vulnerable to cyber-attacks.
Some alarming facts, figures, and statistics on the latest Cyber Security Threats:
- The global average cost of a data breach is USD 3.92 million
- Estimated annual losses through cyberattacks to reach USD 6 Trillion by 2022
- Cybercrime breaches to increase by 76% by 2024
- Over 50% of all global data breaches to occur in the United States by 2023
- The average cost of a data breach to a US company is USD 7.91 million
- The average number of days to identify an incident in 2019 was 206 days
- 2 billion records were exposed due to data breaches in the first half of 2019
- A business will fall victim to a ransomware attack every 11 seconds in 2021
- Cyberattacks on IoT devices increased by 300% in 2019
- Cyberthreat complaints increased by 400% in the US amid the coronavirus pandemic
Consequently, companies and government agencies need maximum cyber security to protect their data and operations. Thus, understanding how to address the latest evolving cyber threats is essential for cyber security professionals. By all means, in order to truly understand these attacks and how their concepts work, let’s go a bit further.
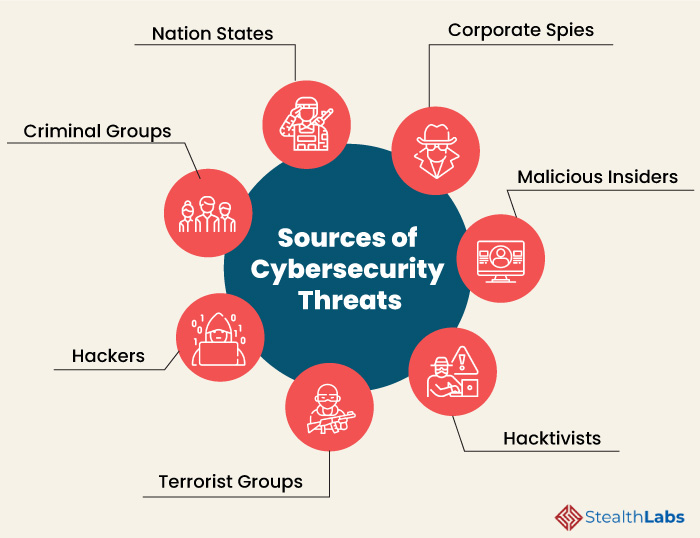
The Key Sources of Cyber Security Threats
From infiltrations on infrastructure and data breaches to spear phishing and brute force, online and cyber threats are so varied. And, they don’t discriminate organizations from individuals when looking for a target. In the 1950s, the word “cyber” referred to cybernetics – the science of understanding the control and movement of machines and animals.
This was followed by “cyber” standing for “computerized.” The 1990s brought around a new cyber-related term. The word “cyberspace” emerged to define an invented physical space. It’s what some people wanted to believe existed behind the electronic activities of computing devices.
According to Microsoft, the pandemic-related phishing and social engineering attacks have skyrocketed to 30,000 per day in the US alone. In order to respond effectively to a cyberattack, it’s imperative to know the threat actors and understand their tactics, techniques, and procedures. Consider the following illustration of key sources:
As a matter of fact, the COVID-19 Pandemic (Coronavirus) emerged as the biggest challenge for businesses and IT organizations in 2020. Amid the pandemic, the cyber threats and data breaches have grown in sophistication and volume. The number of breaches increased 273% in the first quarter, compared to 2019.
Choosing the right online cyber security master’s program is crucial. The best programs offer courses that stay current with today’s cyber security issues and concerns. You can learn more about how UND’s online Master of Science in Cyber Security prepares students for top cyber security careers.
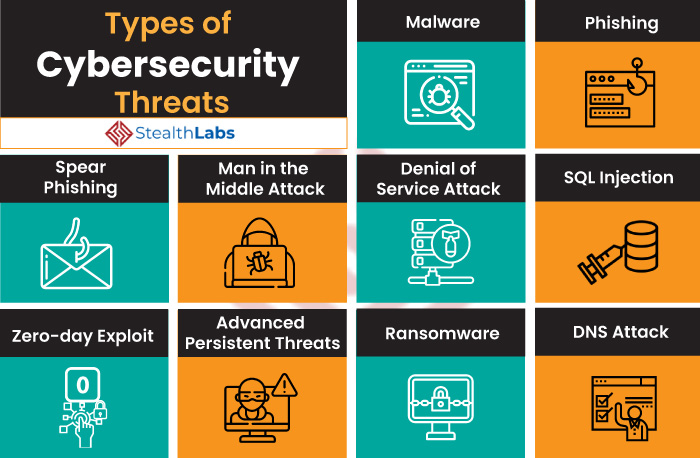
The Major Types of Cyber Security Threats
Corporate Espionage, Business Disruption, or Financial Gain. Whatever the motivation, cybersecurity threats have become pervasive and continue to upend every facet of the digital realm. According to a Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR) by Verizon, 86% of cybersecurity breaches were financially motivated.
While 10% were motivated by espionage. Beyond causing severe financial damage, cyberattacks can lead to regulatory penalties, lawsuits, reputational damage, and business continuity disruptions. Meaning, no business and IT organization are safe in the present cyber world.
Nation-states are the sources of many of the most serious attacks. There are several different versions of nation-state cyber threats. Some are basic espionage — trying to learn another country’s national secrets. Others are aimed at disruption.
In most cases, Cybercriminals increasingly rely on very sophisticated technologies. Thus, organizations often feel hopeless as their confidential data and critical assets fall prey to malicious attacks.
Moreover, the rapid adoption of emerging technologies is contributing too. Including AI, the Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud computing. They all have added new cyber threats for organizations while adding complexity to existing risks. Below are some of the major types of Cyber Security Threats to consider:
1. Malware Attacks & Data Breaches
Chiefly, mobile devices are so vulnerable to malware attacks just like other computing hardware. Attackers may embed malware in app downloads, mobile websites, or phishing emails and text messages. Once compromised, a mobile device can give the malicious actor access to personal information, location data, financial accounts, and more.
Generally, Malware Attacks are the most common type of cyberattack. Malware is malicious software such as spyware, ransomware, viruses, and worms. It’s activated when a user clicks on a malicious link or attachment, which leads to installing dangerous software. Cisco reports that malware, once activated, can:
- Block access to key network components (ransomware)
- Install additional harmful software
- Covertly obtain information by transmitting data from the hard drive (spyware)
- Disrupt individual parts, making the system inoperable
According to Accenture, the average cost of a malware attack is USD 2.6 million. On the other side, a data breach is a theft of data by a malicious actor. Motives for data breaches include crime (i.e. identity theft), a desire to embarrass an institution (e.g. Edward Snowden or the DNC hack), and espionage.
2. Password Attacks
With the right password, a cyber attacker has access to a wealth of information. Social Engineering is a type of password attack that Data Insider defines as “a strategy cyber attackers use that relies heavily on human interaction and often involves tricking people into breaking standard security practices.”
Other types of password attacks include accessing a password database or outright guessing. Likewise, IoT devices like industrial sensors are vulnerable to multiple types of cyber threats. These include hackers taking over the device to make it part of a DDoS attack. Or unauthorized access to data being collected by the device.
Given their numbers, geographic distribution, and frequently out-of-date operating systems, IoT devices are a prime target for malicious actors.
3. Emotet Attack
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) describes Emotet as “an advanced, modular banking Trojan. Primarily, it functions as a downloader or dropper of other banking Trojans. Emotet continues to be among the most costly and destructive malware.”
What made Emotet so dangerous is that the malware was offered for hire to other cybercriminals. Whilst, allowing them to install other types of malware too. Such as banking Trojans or ransomware, onto a victim’s computer. Fortunately, there’s some good news for the Joint Eurojust Europol Press Release that we can all applaud.
In that case, law enforcement and judicial authorities worldwide as of the week of 27 January 2021, disrupted EMOTET from the list of one of the most significant botnets of the past decade. And, as a result, investigators have now taken control of its infrastructure in an international coordinated action (learn more).
4. Ransomware Attack
Basically, a Ransomware Attack is a type of malware infiltration in which the attacker locks or encrypts the victim’s data. And then, they threaten to publish or blocks access to data unless a ransom is paid. It allows a type of malicious software designed to block access to a computer system or computer files.
Most ransomware variants encrypt the files on the affected computer. Thereby, making them inaccessible, and demanding a ransom payment to restore access. There are several different ways that ransomware can infect a computer. One of the most common methods today is through malicious spam or malspam.
On a clear note, a Malspam is an unsolicited email that is used to deliver malware. The email might include booby-trapped attachments, such as PDFs or Word documents. It might also contain links to malicious websites. You can read and learn more about How A Ransomware Attack Occurs in detail.
5. Phishing Attack & Spear Phishing
Phishing attacks use fake communication, such as an email, to trick the receiver into opening it and carrying out the instructions inside, such as providing a credit card number. “The goal is to steal sensitive data like credit card and login information or to install malware on the victim’s machine,” Cisco reports.
In most cases, Cybercriminals send malicious emails that seem to come from legitimate resources. The user is then tricked into clicking the malicious link in the email. As a result, leading to malware installation or disclosure of sensitive information like credit card details and login credentials.
Spear phishing is a more sophisticated form of a phishing attack in which cybercriminals target only privileged users such as system administrators and C-suite executives. More than 71% of targeted attacks involve the use of spear phishing.
6. SQL Injection
A Structured Query Language (SQL) Injection is a type of cyber attack that results from inserting malicious code into a server that uses SQL. It occurs when Cybercriminals attempt to access the database by uploading malicious SQL scripts.
When infected, the server releases information. Submitting the malicious code can be as simple as entering it into a vulnerable website search box. And, once successful, the malicious actor can view, change, or delete data stored in the SQL database. In total, it accounts for nearly 65.1% of all web application attacks.
7. Denial of Service (DoS) Attack
A Denial of Service (DoS) is a type of cyber security attack that floods a computer or network so it can’t respond to requests. A distributed DoS (DDoS) does the same thing, but the attack originates from a computer network. Cyber attackers often use a flood attack to disrupt the “handshake” process and carry out a DoS.
Several other techniques may be used, and some cyber attackers use the time that a network is disabled to launch other attacks. A botnet is a type of DDoS in which millions of systems can be infected with malware and controlled by a hacker, according to Jeff Melnick of Netwrix, an information technology security software company.
Botnets, sometimes called zombie systems, target and overwhelm a target’s processing capabilities. In addition, they are also in different geographic locations and are hard to trace. The year 2019 saw a staggering 8.4 million DDoS attacks.
8. Man in the Middle (MITM) Attack
A Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attack occurs when hackers insert themselves into a two-party transaction. After interrupting the traffic, they can filter and steal data, according to Cisco. MITM attacks often occur when a visitor uses an unsecured public Wi-Fi network.
Attackers insert themselves between the visitor and the network and then use malware to install software and use data maliciously. Once the attacker interprets the communication, they may filter and steal sensitive data and return different responses to the user. According to Netcraft, 95% of HTTPS servers are vulnerable to MITM.
9. DNS Attack & Zero-Day Exploit
A DNS attack is a Cyberattack in which cybercriminals exploit vulnerabilities in the Domain Name System (DNS). The attackers leverage the DNS vulnerabilities to divert site visitors to malicious pages (DNS Hijacking) and exfiltrate data from compromised systems (DNS Tunneling).
Whilst, on the other hand, a Zero-day Attack occurs when software or hardware vulnerability is announced. Eventually, the Cybercriminals exploit the vulnerability before a patch or solution is implemented.
10. Advanced Persistent Threats (APT) & Trojans
An advanced persistent threat occurs when a malicious actor gains unauthorized access to a system or network and remains undetected for an extended time. In reality, 45% of organizations feel that they are likely to be the target of an APT.
Named after the Trojan Horse of ancient Greek history, the Trojan is a type of malware that enters a target system looking like one thing, e.g. a standard piece of software. But then, it lets out the malicious code once inside the host system.
Many cyber threats are bought and sold on the “dark web,” a disorganized but widespread criminal segment of the Internet. In this online bazaar, aspiring hackers can buy ransomware, malware, credentials for breached systems, and more. The dark web serves as a multiplier for threats, with one hacker being able to sell his or her creation over and over.
The Best Practices to Protect from Cybersecurity Attacks
As reliance on digital technologies continues to increase, cyber attacks have become too sophisticated. Thus, organizations that rely on outmoded cybersecurity strategies leave themselves vulnerable to a potential cyberattack.
To prevent these threats, organizations must refine their cybersecurity program. An effective cybersecurity program can help organizations disrupt attacks as they occur, reduce recovery time, and contain future threats. No matter what the level of your cybersecurity maturity, jmexclusives can help you fortify your security stance.
Resource Reference: Ebook | Investing In a Long-term Cloud Security Strategy
With a flexible, practical, and proactive approach to cybersecurity, we can help you navigate the constantly evolving threat landscape. Enterprise best practices for defense from cyber threats include basic but extremely important countermeasures like patching systems.
When a tech vendor discovers (or is informed of) a security flaw in their product, they typically write code that fixes or “patches” the problem. For individuals, the best practices are simple. The good news is that in most cases, some pretty big security organizations stand between the consumer and the hacker.
For instance, the SecOps team at Verizon or AT&T., there are still preventative measures you should take to help ensure your information’s safety.
Consider the following:
- Password hygiene. Big security organizations cannot protect consumers against phishing or hackers who can guess passwords like “1234.” Common sense and password hygiene can go a long way to protect consumers from cyber threats.
- Anti-virus software. Subscribe to anti-virus software and keep your system up to date with automated, scheduled scans.
- Caution against phishing attacks. Be careful about opening file attachments. Phishing and spear-phishing emails are emails that look real but are not. if you pay attention. For instance, if you get an email that says “past due invoice” with a PDF attachment, don’t open it unless you are 100% sure you know who sent it. If you double-check, you’ll probably see it comes from an unusual email.
It can be a scary time for businesses and consumers who are worried about cyber threats. The threats certainly exist, and they’re getting increasingly potent and frequent. The attackers are varied, with many worrisome imbalances between attackers and their targets.
Even if a company is targeted by a powerful nation-state, it is still possible to protect critical digital assets. It takes planning and commitment of resources, but a good security operations team or a proactive individual can stay on top of most of the most serious cyber threats. Below are more practices for your next cyber security strategy:
1. Create an Insider Threat Program
Creating an insider threat program is imperative for organizations to prevent employees from misusing their access privileges to steal or destroy corporate data. The IT security team should not delay and gain the approval of top management to deploy policies across departments.
There are many companies extremely skilled in security, with specific experience in enterprise security. You can read more about outsourcing your security and best practices in this TechTarget article.
2. Train Employees
A host of new technologies and services are coming onto the market that make it easier to mount a robust defense against cyber threats. Employees are the first line of defense against cyber threats for every organization.
Thus, organizations must conduct comprehensive cybersecurity awareness programs to train employees on recognizing and responding to cyber threats. This dramatically improves an organization’s security posture and cyber resilience.
3. Maintain Compliance
Irrespective of the level of cybersecurity an organization implements, it must always maintain compliance with data regulations that apply to its industry and geographical location. The organization must stay abreast with the evolving compliance regulations to leverage the benefits it brings with it.
4. Build a Cyber Incident Response Plan
In the present digital era, no organization is exempt from cyberattacks. Thus, organizations of all sizes must build an effective Cyber Security Incident Response Plan (CSIRP) to navigate cyber adversaries. It enables businesses to prepare for the inevitable, respond to emerging threats, and recover quickly from an attack.
5. Regularly Update Systems and Software
As cyber threats are evolving rapidly, your optimized security network can become outdated within no time, putting your organization at the risk of cyberattack. Therefore, regularly update the security network and the associated systems and software. Also, consider crowdsourced attack simulation/vulnerability testing tools.
There are some excellent, well-vetted companies that offer crowdsourced security services. These teams are professional white hat hackers that can find your company’s vulnerabilities and report them to your security team. Two excellent companies that offer that are Bugcrowd and Hackerone.
6. Backup Data & Initiate Phishing Simulations
Backing up data regularly helps reduce the risk of data breaches. Back up your website, applications, databases, emails, attachments, files, calendars, and more on an ongoing and consistent basis.
Organizations must conduct phishing simulations to educate employees on how to avoid clicking malicious links or downloading attachments. It helps employees understand the far-reaching effects of a phishing attack on an organization.
7. Secure Site with HTTPS
Organizations must encrypt and secure their website with an SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate. HTTPS protects the integrity and confidentiality of data between the user and the website. You can also consider using Threat Detection Tools.
Threat detection tools, also known as XDR (extended detection response), are an essential part of a company’s cybersecurity tech stack. This is considered a level one or first response option to send up a flare whenever something suspicious is found within the company network.
Takeaway,
Phishing attacks are quick and easy to implement and deliver an enormous return on investment, which has motivated criminals to create increasingly sophisticated and creative phishing ‘lures’. These are often indistinguishable from genuine emails, text messages, or phone calls.
In general, affected users don’t report the compromise until it is too late, inflicting enormous damage on your organization. Senior management needs regular assurance that staff has been properly trained on how to spot phishing emails. And the only real way to achieve this is through simulated phishing attack awareness training.
Related Topic: Why Cyber Security Awareness Is Important | Useful Tools
Technically, Internet Security Awareness or Cyber Security Awareness refers to how much end-users know about the Cyber Security Threats their networks face. As well as the risks they introduce, and mitigating security best practices to guide their behavior. Organizations could also seek to reduce the risk of the human element (end users).
Notwithstanding, cyber security threats continue to evolve, causing trillions worth of losses to the cyber world. Meaning, cyber threats are never static. There are millions being created every year. Most threats follow the standard structures described above. However, they are becoming more and more potent.