Tooth Plaque develops when foods containing carbohydrates (sugars and starches), such as milk, soft drinks, raisins, cakes, or candy are frequently left on the teeth. Bacteria that live in the mouth thrive on these foods, producing acids as a result. Over a period of time, these acids destroy tooth enamel, resulting in tooth decay. Plaque can also develop on the tooth roots under the gum.
And then, it causes a breakdown of the bone supporting the tooth. At the end of the day, your body can only tolerate so much. After a certain amount of buildup, your gums get annoyed and throws a hissy fit. Your immune system kicks in with an inflammatory response that tries to attack the germs in the plaque.
As a result, this leads to redness, swelling and bleeding gums around the tooth. This early stage of gum disease is known as gingivitis. So, you can see, if plaque & calculus is left to fester on our teeth for long enough (ie if you don’t brush your teeth twice a day and visit the dentist regularly), it can cause some serious trouble.
What Are Tooth Plaque & Calculus?
On one hand, Tooth Plaque is a colorless, sticky film made up of invisible masses of harmful bacteria. Some of these bacteria cause tooth decay, and then there are different types of germs that cause gum disease. It forms all day, every day from eating and drinking as the germs multiply in your mouth.
So, you’re removing plaque every day when you brush and floss your teeth. On the other hand, Calculus is hardened calcium deposits and dead germs stuck on your teeth. Like barnacles on a boat can be white or stained dark, and you can’t clean it off by yourself.
When plaque builds up around the gums and isn’t cleaned off, it hardens over time. With the help of calcium deposits from our saliva, this plaque turns into calculus. Because calculus is rougher than tooth enamel, even more plaque grabs onto the calculus.
Once there is a new plaque on the calculus, it makes it super difficult for you to brush off. Day by day, more plaque builds up and hardens over time and well – you get the idea!
What are Healthy Gums?
The gums, or gingivae, are composed of pink tissue in the mouth that meets the base of the teeth. There is one gum or gingiva for each set of teeth. The gingival tissue is dense. It has a good supply of blood vessels beneath a moist surface, otherwise known as a mucous membrane.
The gingival tissue connects with the rest of the mouth lining but is pink instead of shiny red. And the gums are firmly attached to the jawbone and tightly cover each tooth up to the neck. When intact, the gums cover the roots of the teeth and protect them.
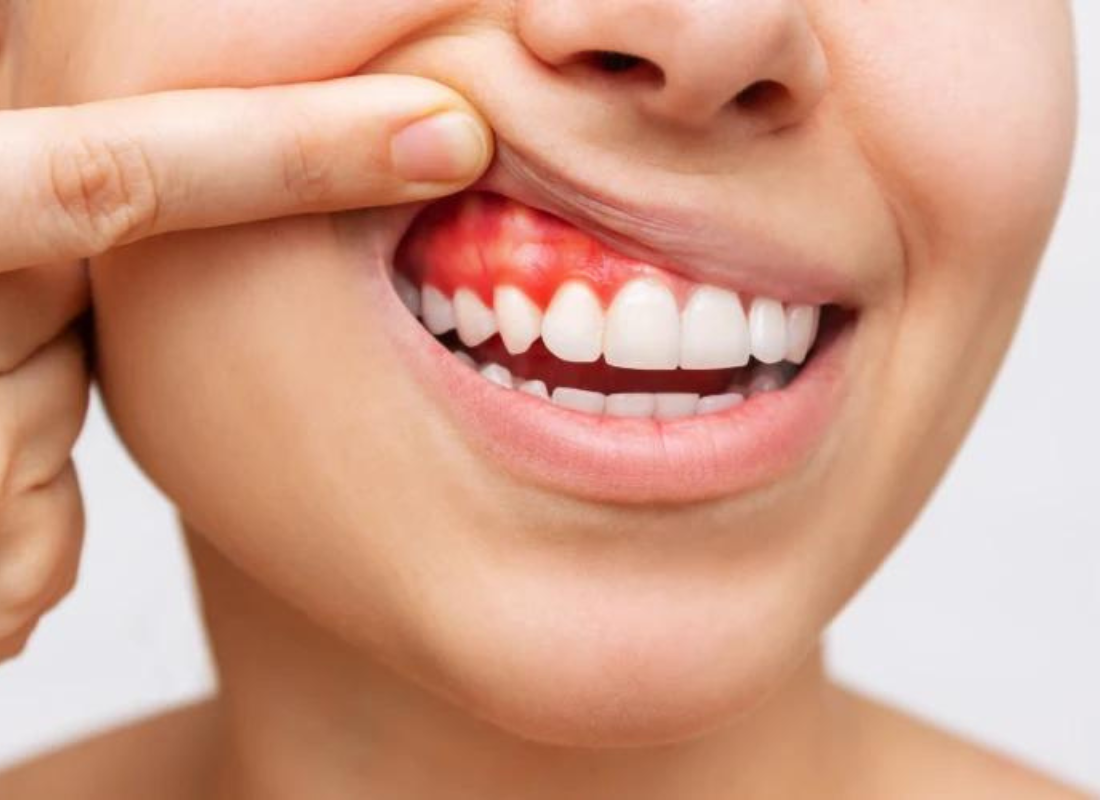
A gingival recession happens after a person has experienced a loss of tissue in the gum. It exposes the fragile roots of the teeth to bacteria and plaque and can lead to decay. Since the gingival recession has direct causes and predisposing factors, orthodontic treatment is able to prevent a recession.
And even contribute to its treatment, with or without a periodontal approach. Depending on the type and severity of gingival tissue damage. However, there is no evidence on the fact that orthodontic treatment alone might induce a gingival recession.
How do you Prevent Plaque formation?
If you don’t maintain healthy gums, you are more likely to have gum disease, which can progress to a number of problems with your teeth and oral health. And as we talked about above, other long-term, chronic health conditions can be associated with periodontitis, a serious form of gum disease.
Notably, gingivitis occurs in 3 out of 4 of Kenyans during their lifetime, but with proper dental care early on, it’s easily reversed. However, if left untreated, gingivitis can develop into a more severe form of gum disease, known as periodontitis. In reality, which is a major cause of tooth loss in adults.

Other factors might increase your risk of gingivitis. If some of the factors below apply to you, pay extra attention to your teeth and gum line. Furthermore, talk to your dentist and hygienist about what you can do. In that case, to keep your mouth healthy and free from gum disease.
Below are the main contributing factors of Gingivitis;
1. Smoking or Tobacco Use
Above all, this is one of the greatest risk factors associated with gum disease. And can lower the chances for successful treatment. Research shows that smokers are seven times more likely to suffer from gum disease than people who don’t smoke.
2. Poor Oral Hygiene
Important to realize, if care is not taken to general hygiene, such as, not brushing or flossing regularly is one of several easily avoided causes of gingivitis.
3. Plaque Removal
You may be missing the plaque found around the gum line, even if the plaque on your teeth has been removed. Be sure to floss regularly and look for a toothpaste like Crest Gum Detoxify or Crest Gum and Enamel Repair that can reach plaque around the gum line.
4. Stress Tiredness
Remarkably, stress is another one of many causes of gingivitis. Constant stress can weaken your immune system and negatively impact your ability to fight infection, including gum disease.
5. Hormonal changes
As an illustration, some hormonal changes may bring about gingivitis. Including, puberty, pregnancy, menopause, and monthly menstruation. Not to mention, they cause increased sensitivity and inflammation in your gums.
Therefore, take extra care of your teeth and gums during these physiological changes to prevent gum disease.
6. Dietary & Poor Nutrition
Poor nutrition or dietary plan deprives the body of important nutrients and makes it more difficult for the body to fight infection, including gum disease.
7. Medications
In general, medication type for many conditions can affect oral health. As soon as you discover some side effects, tell your dentist or hygienist. Particularly, if you take any prescription or over-the-counter medications.
8. Chronic Diseases
For one thing, some chronic diseases such as diabetes, cancer, and HIV, impair the body’s ability to fight infection, including gum disease. Most importantly, tell your dentist and hygienist if you have any medical conditions.
Summing Up,
As a result of Plaque, periodontitis leads the affected teeth (usually mandibular incisors or maxillary canines) to be involved in situations that act as predisposing factors. Allowing direct causes to act and, therefore, trigger recession. Especially when the buccal bone plate is very thin or presents with dehiscence. Learn more about How can orthodontic treatment help?
For most people, the disease progresses slowly over a period of 20 to 30 years, before they start losing teeth. Notably, periodontitis is generally painless until the later stages and many do not know they have problems.
Periodontitis can also cause tooth loss. And some research suggests that the bacteria responsible for periodontitis can enter your bloodstream through the gum tissue. And, possibly affecting your heart, lungs and other parts of your body.
For example, periodontitis may be linked with respiratory disease, rheumatoid arthritis, coronary artery disease or stroke. But more studies are needed to confirm a link.
Resources;
I hope you enjoyed reading the revised guide above on how to maintain healthy gums, therefore, help us share with other readers online. If you have additional contributions, suggestions, and recommendations, please Contact Us. Or even, leave them in the comments box below this post.
All in all, below are more useful and related topic links.
- What Causes Dry Mouth?
- Periodontitis Symptoms & Causes
- 6 Ways to Keep Your Gums Healthy
- Medical Health & Physical Fitness Guides
- Gingivitis » Treatment & Preventive Measures




